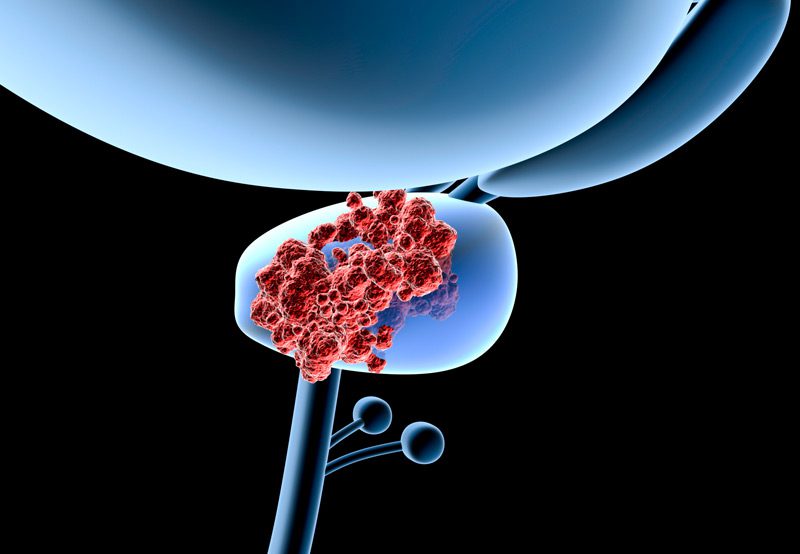
An MRI-guided transperineal prostate biopsy is a precise diagnostic procedure used to detect prostate cancer, particularly in men with elevated PSA levels, abnormal digital rectal exams (DRE), or prior negative biopsies with ongoing suspicion. This technique combines magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with real-time ultrasound and a transperineal approach for improved cancer detection accuracy.
Causes of Prostate Cancer Evaluation
- Elevated PSA: Persistent or rising prostate-specific antigen levels, even with prior negative biopsies, may indicate the need for more accurate evaluation.
- Abnormal DRE: Irregularities felt during a digital rectal exam may prompt biopsy to rule out cancer.
- Prior Negative Biopsy with Ongoing Concern: Men with ongoing symptoms or risk factors despite previous negative results often benefit from MRI-guided biopsy.
- Family History or Genetic Risk: Patients with a strong family history of prostate cancer or BRCA mutations may undergo early and detailed evaluation.

Diagnosis
The MRI-guided transperineal biopsy is typically performed after an MRI identifies areas of concern (PI-RADS lesions) in the prostate. These suspicious regions are targeted during biopsy using a fusion system that overlays MRI data onto real-time ultrasound imaging.
Key diagnostic steps include:
- Pre-biopsy multiparametric MRI
- Evaluation of PI-RADS scoring
- PSA trend monitoring
- Transperineal mapping for systematic and targeted sampling
Treatment Options
This procedure is primarily diagnostic, but its outcomes guide critical treatment decisions. Benefits of the MRI-guided transperineal approach include:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Better sampling of anterior and apical regions of the prostate often missed by transrectal methods.
- Lower Infection Risk: Avoids the rectal wall, reducing the risk of post-biopsy infection.
- Better Cancer Detection: Increases the likelihood of detecting clinically significant cancer while reducing overdiagnosis of indolent tumors.
- Outpatient Procedure: Often performed under local or light sedation in a clinical setting with minimal downtime.
Next Steps
If you have an elevated PSA or ongoing concerns about prostate health, an MRI-guided transperineal prostate biopsy may offer a safer and more accurate diagnosis. Your urologist will review your imaging, lab results, and clinical history to determine if this approach is appropriate. Accurate diagnosis allows for timely decisions regarding treatment or active surveillance, optimizing long-term outcomes.
