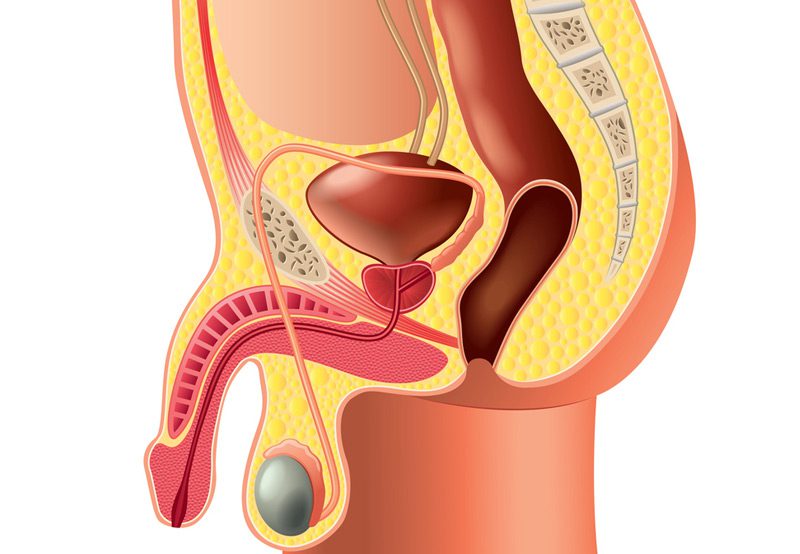
Scrotal surgeries address a range of conditions that affect the scrotum and its contents, including the testicles, epididymis, and spermatic cord. These procedures are commonly performed to treat discomfort, improve fertility, or remove abnormal growths. Depending on the condition, scrotal surgery may be performed under local, regional, or general anesthesia and often involves a short recovery time.
Conditions That May Require Scrotal Surgery
- Hydrocele: Fluid buildup around the testicle that can cause swelling and discomfort. A procedure called hydrocelectomy drains the fluid and prevents recurrence.
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins within the scrotum that may contribute to infertility or discomfort. A varicocelectomy removes or ties off the affected veins to improve blood flow.
- Spermatocele: A fluid-filled cyst in the epididymis that may require excision if it becomes painful or enlarges.
- Testicular Torsion: A surgical emergency where the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood flow to the testicle. Immediate surgery is necessary to preserve testicular function.
- Epididymal Cyst or Mass: Removal may be recommended if the cyst is painful, large, or suspicious for malignancy.
- Testicular Cancer: If a testicular mass is suspicious, an inguinal orchiectomy (removal of the testicle through a groin incision) may be performed for diagnosis and treatment.
- Chronic Scrotal Pain: In select cases, microsurgical procedures on the spermatic cord (e.g., cord denervation) may be used to relieve long-standing pain.

Surgical Approach
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Many scrotal surgeries are done through small incisions with minimal tissue disruption, leading to faster recovery.
- Outpatient Basis: Most procedures are completed as day surgeries, with patients returning home the same day.
- Anesthesia Options: Depending on the surgery and patient preference, local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia may be used.
Recovery and Outcomes
- Postoperative Care: Patients are advised to rest, wear supportive underwear, and apply ice to reduce swelling.
- Downtime: Most individuals resume light activities within a few days and return to full activity within 1–2 weeks.
- Fertility Preservation: For conditions affecting fertility (such as varicocele), surgery can improve semen parameters and reproductive outcomes.
- Low Risk of Complications: When performed by experienced urologists, scrotal surgeries carry a low risk of infection, bleeding, or recurrence.
Next Steps
If you are experiencing scrotal discomfort, swelling, or changes in testicular size or shape, consult with a urologist. Scrotal surgery may offer effective relief and improve both comfort and function, especially when tailored to your specific diagnosis and reproductive goals.
